(S1.4) Functional Selectivity and Drug discovery for Novel Psychedelic Anti-Inflammatories
Speakers
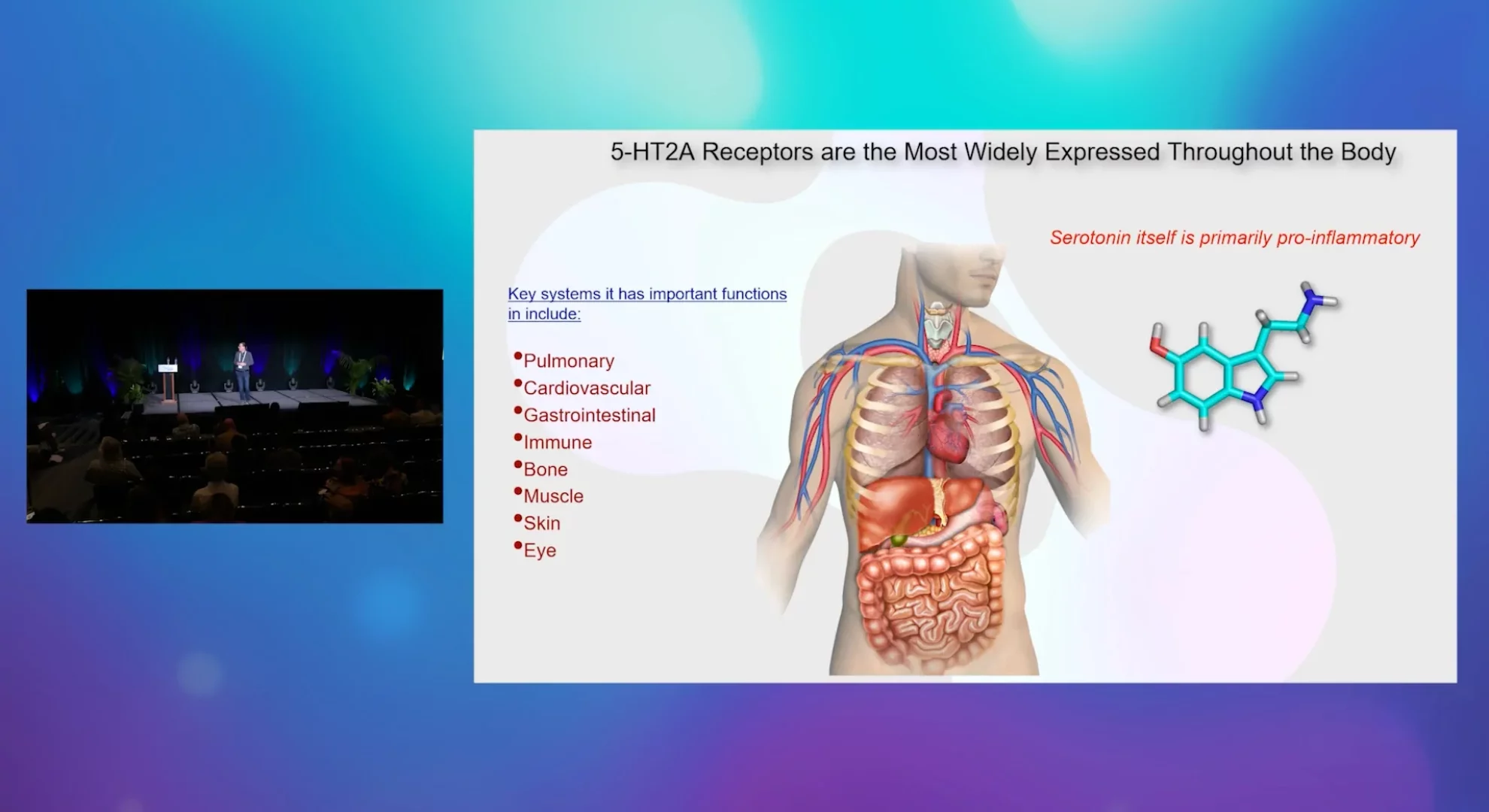
Some psychedelics and agonists of 5-HT2A receptors demonstrate potent anti-inflammatory effects in models of human disease such as asthma. However, other psychedelics and agonists at 5-HT2A receptors are devoid of anti-inflammatory activity despite having powerful behavioral effects. We have conducted a structure-activity relationship analysis of several psychedelics and have found that behavioral activity and effects do not correlate with anti-inflammatory efficacy, nor does coupling with effector signaling pathways believed to underlie behavioral effects. Using ‘psychedelic anti-inflammatories’ and ‘psychedelic non anti-inflammatories’ as tools we have identified potential key cellular mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of psychedelic anti-inflammatories. Further, we have begun leveraging this information to design new 5-HT2A ligands that potentially retain full anti-inflammatory efficacy but have reduced behavioral effects.
Share: (S1.4) Functional Selectivity and Drug discovery for Novel Psychedelic Anti-Inflammatories
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Email




